2016 Election Results Senate and House of Representatives
| ← 2014 2015 2016 2017 2022 → Presidential ballot year | |
| Election twenty-four hour period | November 8, 2016 |
|---|---|
| Incumbent president | Barack Obama (Autonomous) |
| Adjacent Congress | 115th |
| Presidential ballot | |
| Partisan control | Republican gain |
| Popular vote margin | Democratic +two.1% |
| Electoral vote | |
| Donald Trump (R) | 304 |
| Hillary Clinton (D) | 227 |
| Others | 7 |
| | |
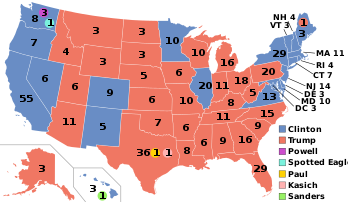
| Presidential election results map. Cerise denotes states won by Trump/Pence, blue denotes states won past Clinton/Kaine. Numbers indicate electoral votes allotted to the winner of each state. 7 faithless electors cast votes for various individuals. | |
| Senate elections | |
| Overall command | Republican concur |
| Seats contested | 34 of 100 seats |
| Net seat change | Democratic +2 |
| | |
| 2016 Senate results Democratic agree Republican hold Democratic gain | |
| House elections | |
| Overall command | Republican agree |
| Seats contested | All 435 voting-members and vi not-voting delegates |
| Popular vote margin | Republican +1.i% |
| Net seat change | Democratic +6 |
 | |
| Map of the 2022 House races (consul races not shown) Democratic hold Republican concord Democratic gain Republican gain | |
| Gubernatorial elections | |
| Seats contested | 14 (12 states, two territories) |
| Net seat change | Republican +2 |
| | |
| Map of the 2022 gubernatorial elections Democratic hold Republican hold Democratic proceeds Republican gain New Progressive gain Nonpartisan | |

The 2016 Us elections were held on Tuesday, November 8, 2016. Republican nominee Donald Trump defeated Democratic old Secretary of State Hillary Clinton in the presidential election, while Republicans retained control of Congress. This marked the starting time (and, as of 2020, most recent) fourth dimension Republicans won or held unified control of the presidency and Congress since 2004.
Trump won his political party's nomination after defeating Ted Cruz and several other candidates in the 2022 Republican presidential primaries. With Autonomous president Barack Obama term-express, Clinton defeated Bernie Sanders in the 2022 Democratic presidential primaries. Trump won the general ballot with 304 of the 538 electoral votes, though Clinton won the popular vote past a margin of 2.1 per centum points (2,868,686 votes). The United States regime's intelligence agencies later ended that the Russian regime had interfered in the elections.
Wall Street banks and other big financial institutions spent a record $2 billion trying to influence the 2022 United states elections.[1] [two]
Democrats won a net gain of 2 seats in the Senate and half-dozen seats in the House of Representatives, only Republicans retained command of both chambers. In the gubernatorial elections, Republicans won a net gain of two seats. Diverse other state, territorial, and local races and referenda were held throughout the year.
Federal elections [edit]
Presidential election [edit]
The United states presidential election of 2022 was the 58th quadrennial presidential election. The electoral vote distribution was adamant by the 2010 census from which presidential electors electing the president and vice president were chosen; a elementary majority (270) of the 538 balloter votes were required to win. In 1 of the greatest election upsets in U.South. History, man of affairs and reality television personality Donald Trump of New York won the Republican Political party's presidential nomination on July xix, 2016, after defeating Texas Senator Ted Cruz, Ohio Governor John Kasich, Florida Senator Marco Rubio, and several other candidates in the Republican primary elections.[1] Former Secretarial assistant of State, First Lady and New York Senator Hillary Clinton won the Autonomous Party's presidential nomination on July 26, 2016, after defeating Vermont Senator Bernie Sanders and others in the Democratic primary elections. This was the kickoff ballot with a female person presidential nominee from a major political party, also equally the get-go election since 1944 that had major party presidential nominees from the same domicile land. Clinton won the popular vote, taking 48% of the vote compared to Trump'south 46% of the vote, only Trump won the balloter vote and thus the presidency. Libertarian Gary Johnson won iii.three% of the pop vote, the strongest performance by a third political party presidential nominee since the 1996 election. Trump won u.s.a. of Michigan, Pennsylvania, Wisconsin, Florida, Ohio, and Iowa, all of which were won past Obama in 2008 and 2012. The election is one of v presidential elections in American history in which the winner of the popular vote did not win the presidency.
Russian interference [edit]
The United States authorities'due south intelligence agencies concluded the Russian regime interfered in the 2022 United States elections.[iii] [4] A joint US intelligence review stated with high confidence that, "Russian President Vladimir Putin ordered an influence campaign in 2022 aimed at the U.s. presidential ballot. In May 2019, Republican Florida Governor Ron DeSantis announced Russians hacked voting databases in two Florida counties prior to the 2022 presidential election and no election results were compromised.[v] [6] [7]
Congressional elections [edit]
Senate elections [edit]
All seats in Senate Class 3 were up for election. Democrats won a cyberspace gain of 2 seats, merely Republicans retained a bulk with 52 seats in the 100-member chamber.[8]
Business firm of Representatives elections [edit]
All 435 voting seats in the United States House of Representatives were up for election. Additionally, elections were held to select the delegates for the Commune of Columbia and the U.Southward. territories, including the Resident Commissioner of Puerto Rico.
Democrats won a net proceeds of 6 seats, but Republicans held a 241-to-194 majority following the elections. Nationwide, Republicans won the popular vote for the House of Representatives past a margin of 1.1 percent.[9]
State elections [edit]
Gubernatorial elections [edit]
Regular elections were held for the governorships of 11 U.Southward. states and 2 U.Due south. territories. Additionally, a special ballot was held in Oregon after the resignation of John Kitzhaber as governor. Republicans won a cyberspace proceeds of two seats.
Legislative elections [edit]
In 2016, 44 states held country legislative elections; 86 of the 99 chambers were upwardly for election. Only six states did not concur state legislative elections: Louisiana, Mississippi, New Jersey, Virginia, Alabama, and Maryland.[10]
Other elections and ballot measures [edit]
Many states also held elections for other elected offices, such equally attorney full general. Many states held ballot measures.[xi]
Local elections [edit]
Mayoral elections [edit]
Mayoral elections were held in many cities, including:
- Bakersfield, California: Incumbent Harvey Hall did non seek re-ballot.[12] Karen Goh was elected to succeed Hall. The part is non partisan.
- Baltimore, Maryland: Incumbent Democrat Stephanie Rawlings-Blake did not seek re-election.[13] Democrat Catherine E. Pugh was elected as Rawlings-Blake's replacement.
- Gilbert, Arizona: Incumbent John Lewis resigned prior to the election.[14] Interim mayor Jenn Daniels was elected to succeed Lewis. The office is not partisan.
- Honolulu, Hawaii: Incumbent Democrat Kirk Caldwell won re-election to a second term.
- Milwaukee, Wisconsin: Incumbent Tom Barrett was re-elected to a fourth term. The office is not partisan.
- Portland, Oregon: Incumbent Charlie Hales did not seek re-election.[15] Ted Wheeler was elected to succeed Hales. The office is not partisan.
- Richmond, Virginia: Incumbent Dwight C. Jones was term-limited and cannot seek re-ballot. Levar Stoney was elected as the new Richmond, VA, mayor. The office is not partisan.
- Sacramento, California: Incumbent Democrat Kevin Johnson did non seek re-election.[xvi] Democrat Darrell Steinberg was elected every bit Johnson's replacement.[17]
- San Diego, California: Incumbent Kevin Faulconer won a second term every bit mayor. The function is not partisan.
- Tulsa, Oklahoma: Incumbent Republican Dewey F. Bartlett Jr. was defeated by city councilor and swain Republican G. T. Bynum.[18]
Table of land, territorial, and federal results [edit]
This tabular array shows the partisan results of Congressional, gubernatorial, presidential, and state legislative races held in each state and territory in 2016. Note that not all states and territories concur gubernatorial, state legislative, and United States Senate elections in 2016; additionally, the territories do non have electoral votes in American presidential elections, and neither Washington, D.C. nor the territories elect members of the United states of america Senate. Washington, D.C., and the five inhabited territories each elect one non-voting fellow member of the United States House of Representatives. Nebraska's unicameral legislature and the governorship and legislature of American Samoa are officially non-partisan. In the table, offices/legislatures that are non up for election in 2022 are already filled in for the "afterwards 2022 elections" department, although vacancies or party switching could potentially lead to a flip in partisan control.
| Subdivision and PVI[19] | Before 2022 elections[xx] | After 2022 elections[21] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subdivision | PVI | Governor | Country leg. | U.s.a. Senate | US House | Pres. | Governor | Land leg. | United states Senate | United states of america House |
| Alabama | R+14 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 6–1 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 6–i |
| Alaska | R+12 | Ind | Rep | Rep | Rep 1–0 | Rep | Ind | Rep | Rep | Rep 1–0 |
| Arizona | R+7 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 5–iv | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 5–4 |
| Arkansas | R+14 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep four–0 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep four–0 |
| California | D+9 | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem 39–xiv | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem 39–14 |
| Colorado | D+1 | Dem | Split | Split | Rep 4–3 | Dem | Dem | Divide | Carve up | Rep 4–3 |
| Connecticut | D+seven | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem 5–0 | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem v–0 |
| Delaware | D+viii | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem 1–0 | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem 1–0 |
| Florida | R+two | Rep | Rep | Split | Rep 17–10 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Split | Rep 16–11 |
| Georgia | R+6 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 10–4 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep x–4 |
| Hawaii | D+20 | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem two–0 | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem 2–0 |
| Idaho | R+18 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 2–0 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep two–0 |
| Illinois | D+eight | Rep | Dem | Carve up | Dem 10–8 | Dem | Rep | Dem | Dem | Dem xi–7 |
| Indiana | R+v | Rep | Rep | Split | Rep 7–ii | Rep | Rep | Rep | Split | Rep vii–ii |
| Iowa | D+1 | Rep | Divide | Rep | Rep 3–1 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep iii–1 |
| Kansas | R+12 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 4–0 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 4–0 |
| Kentucky | R+thirteen | Rep | Separate | Rep | Rep 5–i | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 5–1 |
| Louisiana | R+12 | Dem | Rep | Rep | Rep five–one | Rep | Dem | Rep | Rep | Rep 5–i |
| Maine | D+5 | Rep | Split | Split R/I [a] | Split 1–ane | Dem | Rep | Split | Split R/I [a] | Carve up 1–1 |
| Maryland | D+10 | Rep | Dem | Dem | Dem 7–1 | Dem | Rep | Dem | Dem | Dem vii–i |
| Massachusetts | D+10 | Rep | Dem | Dem | Dem ix–0 | Dem | Rep | Dem | Dem | Dem 9–0 |
| Michigan | D+4 | Rep | Rep | Dem | Rep 9–5 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Dem | Rep 9–v |
| Minnesota | D+2 | Dem | Split | Dem | Dem 5–3 | Dem | Dem | Rep | Dem | Dem 5–3 |
| Mississippi | R+9 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 3–ane | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 3–1 |
| Missouri | R+5 | Dem | Rep | Split | Rep 6–ii | Rep | Rep | Rep | Split | Rep 6–2 |
| Montana | R+7 | Dem | Rep | Split up | Rep ane–0 | Rep | Dem | Rep | Divide | Rep one–0 |
| Nebraska | R+12 | Rep | NP | Rep | Rep two–1 | Rep | Rep | NP | Rep | Rep iii–0 |
| Nevada | D+2 | Rep | Rep | Divide | Rep 3–one | Dem | Rep | Dem | Dissever | Dem 3–one |
| New Hampshire | D+1 | Dem | Rep | Split | Split 1–1 | Dem | Rep | Rep | Dem | Dem 2–0 |
| New Jersey | D+6 | Rep | Dem | Dem | Split half-dozen–6 | Dem | Rep | Dem | Dem | Dem 7–5 |
| New Mexico | D+4 | Rep | Dissever | Dem | Dem 2–i | Dem | Rep | Dem | Dem | Dem 2–1 |
| New York | D+xi | Dem | Dissever [b] | Dem | Dem eighteen–9 | Dem | Dem | Carve up | Dem | Dem 18–nine |
| North Carolina | R+3 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 10–3 | Rep | Dem | Rep | Rep | Rep 10–3 |
| Northward Dakota | R+ten | Rep | Rep | Split | Rep 1–0 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Split | Rep 1–0 |
| Ohio | R+1 | Rep | Rep | Split | Rep 12–4 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Carve up | Rep 12–iv |
| Oklahoma | R+nineteen | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep five–0 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep five–0 |
| Oregon | D+5 | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem 4–i | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem iv–1 |
| Pennsylvania | D+ane | Dem | Rep | Dissever | Rep 13–5 | Rep | Dem | Rep | Dissever | Rep xiii–5 |
| Rhode Isle | D+11 | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem ii–0 | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem | Dem two–0 |
| South Carolina | R+viii | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep half dozen–ane | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 6–1 |
| South Dakota | R+x | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 1–0 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 1–0 |
| Tennessee | R+12 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 7–ii | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep vii–ii |
| Texas | R+10 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 25–eleven | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 25–11 |
| Utah | R+22 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 4–0 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 4–0 |
| Vermont | D+xvi | Dem | Dem | Dissever D/I [c] | Dem 1–0 | Dem | Rep | Dem | Separate D/I [c] | Dem 1–0 |
| Virginia | Even | Dem | Rep | Dem | Rep 8–3 | Dem | Dem | Rep | Dem | Rep seven–4 |
| Washington | D+5 | Dem | Split [b] | Dem | Dem 6–4 | Dem | Dem | Split | Dem | Dem 6–4 |
| West Virginia | R+xiii | Dem | Rep | Split up | Rep 3–0 | Rep | Dem | Rep | Split | Rep 3–0 |
| Wisconsin | D+2 | Rep | Rep | Divide | Rep 5–3 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Split | Rep 5–3 |
| Wyoming | R+22 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 1–0 | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep | Rep 1–0 |
| Us | Even | Rep 31–18 | Rep 30–11 | Rep 54–46[d] | Rep 247–188 | Rep | Rep 33–16 | Rep 32–13 | Rep 52–48[d] | Rep 241–194 |
| Washington, D.C. | D+40 | Dem[eastward] | Dem | N/A | Dem | Dem | Dem[due east] | Dem | Northward/A | Dem |
| American Samoa | N/A | NP/I[f] | NP | Rep | North/A | NP/D [one thousand] | NP | Rep | ||
| Guam | Rep | Dem | Dem | Dem[h] | Rep | Dem | Dem | |||
| Northward. Mariana Islands | Rep | Dissever | Ind[i] | N/A | Rep | Rep | Ind[i] | |||
| Puerto Rico | PDP/D[j] | PDP | PNP/D[yard] | PNP/D[50] | PNP | PNP/R [m] | ||||
| U.South. Virgin Islands | Ind | Dem | Dem | Ind | Dem | Dem | ||||
| Subdivision | PVI | Governor | State leg. | Usa Senate | US House | Pres. | Governor | Land leg. | US Senate | US House |
| Subdivision and PVI | Before 2022 elections | Later on 2022 elections | ||||||||
Footnotes [edit]
- ^ a b 1 of Maine's Senators is a Republican, the other (Angus King) is an contained who has caucused with the Democrats since taking role in 2013.
- ^ a b In New York and Washington, Democrats control the House and a coalition of Republicans and Democrats command the Senate.
- ^ a b Ane of Vermont's Senators is a Democrat, the other (Bernie Sanders) was elected as an independent only has caucused with the Democrats since taking function in 2007.
- ^ a b Including two Independents who caucus with the Democrats.
- ^ a b Washington, D.C. does non elect a governor, merely it does elect a mayor.
- ^ Although elections for governor of American Samoa are non-partisan, Governor Lolo Matalasi Moliga was an Independent when first elected governor in 2014.
- ^ With the 2022 election, Governor Lolo Matalasi Moliga affiliated himself with the Democratic Party at the national level.
- ^ Although Guam does not have a vote in the Electoral Higher, the territory has held a presidential advisory vote for every presidential election since 1980.
- ^ a b Consul Gregorio Sablan was elected as an contained, only he has caucused with the Democrats since taking office in 2009.
- ^ Governor Alejandro García Padilla is a fellow member of the Popular Democratic Party, but also affiliates with the Democratic Party at the national level.
- ^ Resident Commissioner Pedro Pierluisi is member of the New Progressive Party, merely he has caucused with the Democrats since taking office in 2009.
- ^ Governor Ricardo Rosselló is a member of the New Progressive Political party, but also affiliates with the Democratic Party at the national level.
- ^ Resident Commissioner Jenniffer González is fellow member of the New Progressive Party, but she has caucused with the Republicans since taking office in 2017.
References [edit]
- ^ "Wall Street spends tape $2bn on United states of america election lobbying". Financial Times. March 8, 2017.
- ^ "Wall Street Spent $two Billion Trying to Influence the 2022 Election". Fortune. March 8, 2017.
- ^ Miller, Greg; Entous, Adam. "Declassified written report says Putin 'ordered' endeavour to undermine faith in U.S. ballot and aid Trump". Washington Postal service.
- ^ Eichenwald, Kurt (January 10, 2017). "Trump, Putin and the subconscious history of how Russian federation interfered in the U.Southward. presidential election". Newsweek.
- ^ "Gov. DeSantis: Russians hacked voting databases in two Florida counties; The GOP governor said the incidents took place in 2022 and no election results were compromised". NBC News. Associated Press. May 14, 2019. Retrieved May 15, 2019.
- ^ Farrington, Brendan (May 14, 2019). "DeSantis: Russians accessed 2 Florida voting databases". apnews.com. Retrieved May xv, 2019.
- ^ Parks, Miles (May 14, 2019). "Florida Governor Says Russian Hackers Breached 2 Counties In 2016". NPR.org . Retrieved May 16, 2019.
- ^ "Statistics of the Presidential and Congressional Election of November 8, 2016". U.S. Business firm of Reps, Office of the Clerk. Retrieved April 10, 2017.
- ^ "Election Statistics, 1920 to Present". Usa Firm of Representatives. 2016. p. 84.
- ^ Warnock, Kae (March 11, 2016). "2016 Legislative Races by State and Legislative Sleeping accommodation". National Conference of Land Legislatures. Retrieved May 17, 2016.
- ^ "2016 Presidential Election". The American Presidency Project. Retrieved Apr 10, 2017.
- ^ Mayer, Steven. "Karen Goh installed as mayor of Bakersfield". The Bakersfield Californian. Retrieved Jan 17, 2017.
- ^ "Baltimore Mayor Rawlings-Blake says she won't seek re-election". Fox News . Retrieved September 14, 2015.
- ^ Gossie, Michael (July 15, 2017). "Almost Influential Women: Jenn Daniels, Town of Gilbert". AZ Big Media. Retrieved Jan 17, 2018.
- ^ Theen, Andrew (October 26, 2015). "Portland Mayor Charlie Hales withdraws re-election bid". OregonLive. Retrieved Dec 27, 2015.
- ^ "Mayor Kevin Johnson won't seek re-election". Sacramento Bee . Retrieved April 18, 2017.
- ^ "Steinberg wins Sacramento mayor's race by wide margin". Sacramento Bee . Retrieved Apr xviii, 2017.
- ^ "GT Bynum Defeats Incumbent Bartlett For Tulsa Mayor". NewsOn6.com. June 28, 2016. Retrieved January 17, 2018.
- ^ "Partisan Voter Index by State, 1994–2014" (PDF). Cook Political Report . Retrieved May 19, 2016. PVI in 2014
- ^ "2016 State and Legislative Partisan Limerick" (PDF). National Conference of State Legislatures. Retrieved May 17, 2016.
- ^ "State & Legislative Partisan Limerick (2016 Ballot)" (PDF). National Conference of State Legislatures. Retrieved January four, 2016.
External links [edit]
- "State Elections Legislation Database", Ncsl.org, Washington, D.C.: National Conference of State Legislatures,
State legislation related to the administration of elections introduced in 2011 through...2020
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2016_United_States_elections



0 Response to "2016 Election Results Senate and House of Representatives"
Enregistrer un commentaire